Recent Publications
Host-guest mediated controlled release of 5-fluorouracil by CQD integrated starch based smart tripolymeric hydrogel
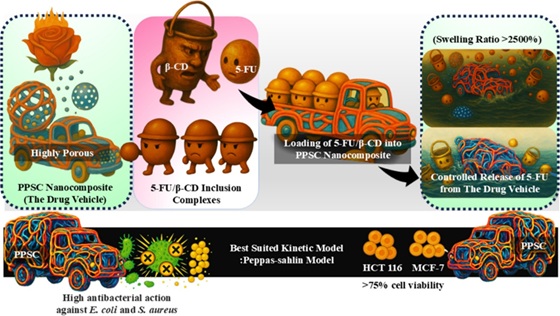
Nowadays, the controlled release of drugs by nanostructured polymeric nanocomposite hydrogels with host-guest mechanism is a big challenge. Herein, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is taken as a model drug and β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) is employed as host for the formation of inclusion complex. Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) prepared from red rose petals are incorporated within the matrix of polyacrylic acid/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/starch to fabricate the PPSC nanocomposite hydrogel. FTIR, XPS, FESEM, HRTEM and XRD techniques are implemented to investigate the spectroscopic and microscopic characterization of hydrogels. The high swelling capacity of PPSC nanocomposite hydrogel exceeding 2500% is due to the porous nature. Further, PPSC hydrogel shows strong antibacterial effects against E. coli and S. aureus and displays over 75% cell viability on both HCT 116 and MCF-7 cell line, denoting the good biocompatible nature. Moreover, drug administration scrutinization of β-FU (β-CD and 5-FU inclusion complex) loaded PPSC exhibits a sustainable prolong release profile, with only 8.9% of the drug released over 6 h. Kinetic analysis of drug administration profile is fitted with the Peppas-Sahlin model for prediction of release mechanism.
Multifunctional h-BN/TiO2 reinforced polyaniline/PVA nanocomposite films for smart antibacterial and flame retardant packaging
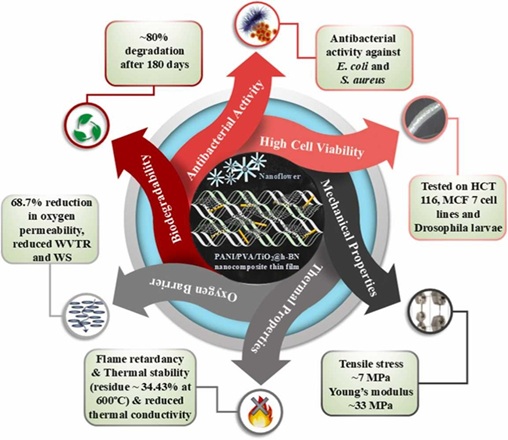
Herein, PANI/PVA nanocomposite (NC) thin films are engineered by incorporating TiO2 and h-BN nanofillers for advanced antibacterial packaging applications. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM) reveals a nanoflower arrangement of TiO2 and h-BN nanofillers within the matrix and the h-BN platelets are strategically laminated within the NC, leading to superior flame retardancy and barrier properties with a 68.7% reduction in oxygen permeability at 5wt% of h-BN loading in comparison to pristine PANI/PVA films. The NC exhibit enhanced thermal stability with a final residue of 34.43% at 600°C, reduced thermal conductivity, and improved mechanical properties, including a tensile stress of ~7MPa and Young's modulus of ~33MPa. The films also reveal reduced water vapor transmission rate (WVTR), water solubility (WS), and efficient degradation up to 80% after 180 days in activated sludge water and increased stability in alkaline environments. Bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus is confirmed, making the films highly effective in inhibiting bacterial growth. In vitro cytotoxicity assays on HCT 116 (colon carcinoma) and MCF 7 (breast cancer) cell lines using the MTT assay, along with in vivo cytotoxicity studies on Drosophila larvae, indicate low toxicity, supporting the safety of the films for active packaging applications.
Graphene Based Nanocomposites: A State of the Art in Heavy Metal Detection
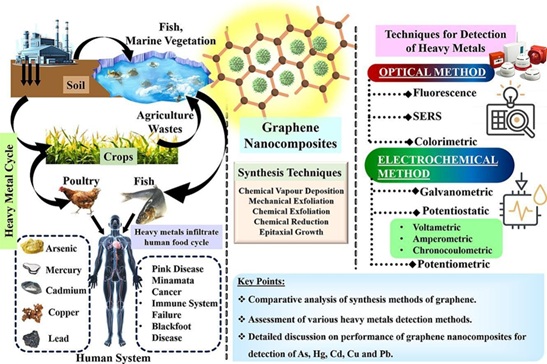
A massive rise in anthropogenic activities in the last few decades has substantially exposed human life to different heavy metal (HM) with high toxicological implications, when present over permissible limits. Hence, detection of these elements, even in trace amounts, becomes pivotal for maintaining quality of life. Several materials have been employed to serve this purpose, out of which graphene and its nanocomposites have exhibited true potential in detection of HM ions present in various environmental and food samples with very minimal limit of detection (LOD). The excellent large surface area, optical, electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties of graphene bestow the hybrid materials with true potential to serve as appropriate sensing platforms for HM ions. This review provides a concise view towards graphene, its derivatives, detection methods, and utilization of graphene in sensing of mercury, arsenic, cadmium, lead, and copper ions in different media. Latest development of smart graphene-based nanostructured biosensors in the last decade, which reveal extraordinary selectivity and sensitivity towards these hazardous substances with unparalleled stability enabling them an essential tool in the field of environmental remediation, are also highlighted in this review.
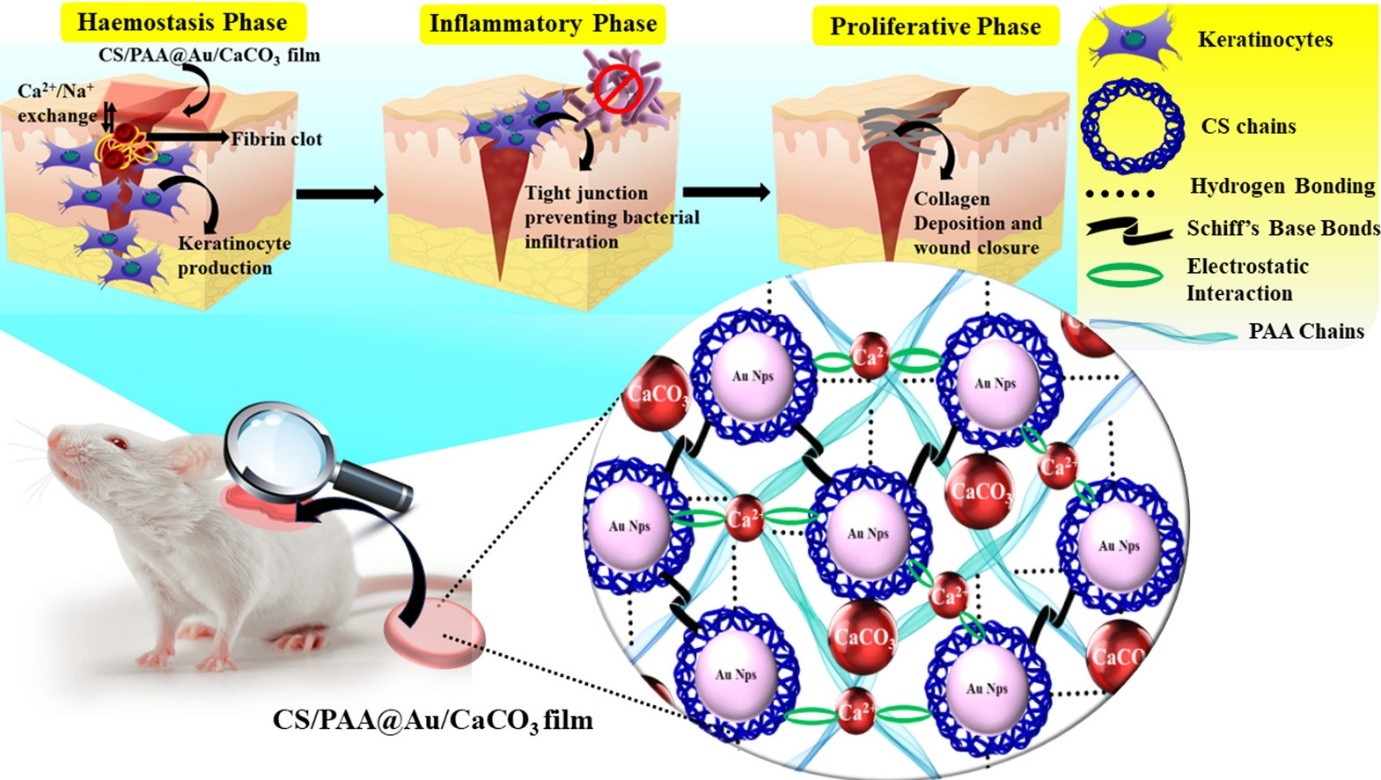
Nano CaCO3 mediated in vitro and in vivo wound healing characteristics of chitosan films without added drugs
This investigation aims towards introducing a facile and cost-effective chitosan-based material for healing of full thickness wounds via stimulation of keratinocyte at wound junction to yield faster closure. Chitosan (CS) crosslinked polyacrylic acid (PAA) polymeric networks are chosen as the matrix element to incorporate gold nanoparticles (Au Nps) and nano calcium carbonate (CaCO3 Nps) via covalent and electrostatic interactions. The as-synthesized CS/PAA@Au/CaCO3 nanocomposite hydrogels reveal high in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility against human kidney epithelial (HKE) cells and drosophila larvae, with minimum cell viability of 88.45 % at high doses of 87.5 μg/μL. The innate pH responsive swelling behaviour (1450 %) and WVTR (8.451 mg·cm−2·h−1), hemocompatibility, bioadhesivity along with antibacterial and anti-biofilm activity of the nanocomposite hydrogels against S. aureus and E. coli provide prior motivation to escalate the study towards in vivo wound healing in invertebrates (D.melanogaster) and vertebrates (Sprague-Dawley rats). The proposed hydrogels show accelerated healing in invertebrates and vertebrates, i.e., complete recovery in 3 h and 11 days, respectively. The histopathology analysis establishes the deposition of highly aligned collagen fibers on the wound surface supported by the tight keratinocyte junction at wound surface by the action of calcium ions for which the material becomes promising for wound healing applications.
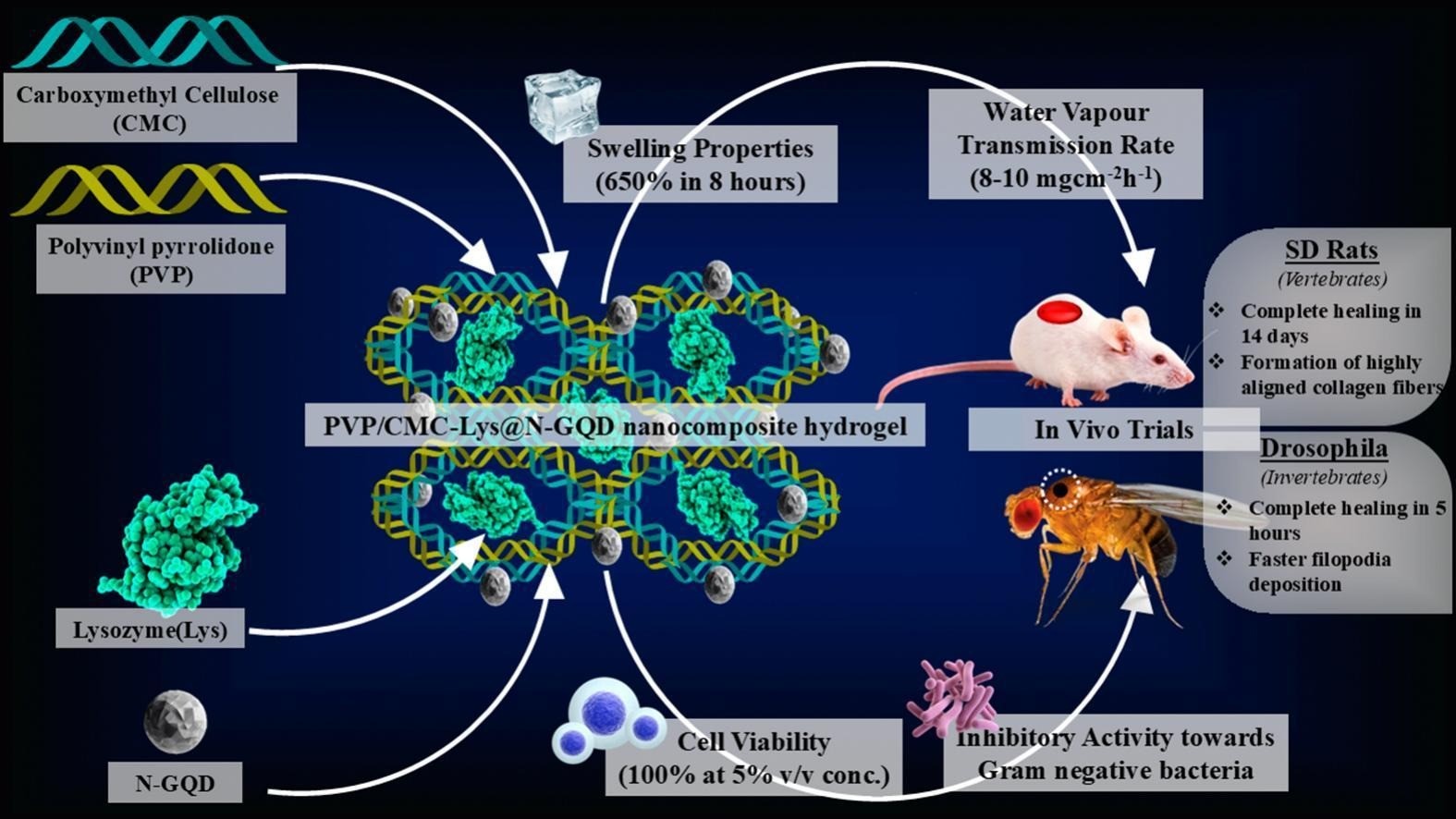
Lysozyme/N-GQD loaded carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels for healing of excision wounds in Drosophila and Sprague Dawley rats
Delayed healing and fibrosis at the wound site present significant challenges in the wound care industry, often leading to complications such as infections, chronic wounds, and impaired tissue regeneration. Therefore, there is a critical need for advanced wound dressing materials that promote faster healing, prevent bacterial infections, and support effective tissue repair. This study aims to develop a Lysozyme (Lys)-based wound dressing with enhanced wound closure rates by incorporating nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) as a functionalized nanofiller to strengthen its antibacterial properties. The wound dressing, formulated with a carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) crosslinked polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) matrix, creates a porous structure that enhances swelling capacity and water vapor transmission rates (WVTR), while cytotoxicity studies confirm its biocompatibility, showing 100 % cell viability in HCT 116 and MCF7 cell lines. The in vivo wound healing performance of the designed nanocomposite hydrogel reflects complete wound closure in 5 h for Drosophila Melanogaster, aided by the shorter life span and faster metabolic processes in Drosophila, and 14 days in Sprague Dawley rat models. These results qualify the material as a promising candidate for wound dressing applications, bridging the gap between material science and medical science for effective wound management.
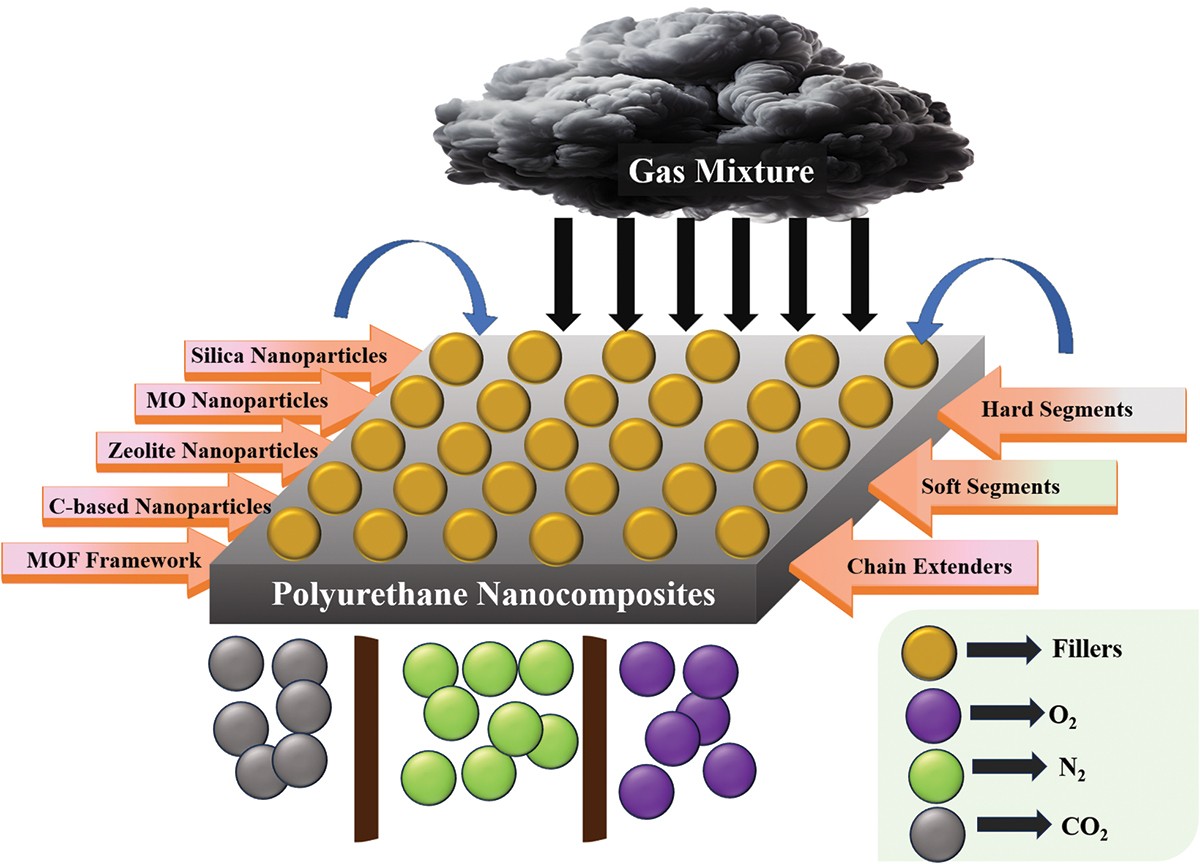
Polyurethane Nanocomposite for Gas Separation: A Review
Due to its remarkable characteristics, such as small environmental footprint, design, low cost and ease of use, polyurethane (PU) nanocomposites have been regarded as a promising material for effective gas separation (GS). The primary influencing elements on the GS performance and gas transport characteristics of these membranes are closely elaborated in this review. The recent developments in PU-based nanocomposites with a focus on enhanced gas permeability and selectivity are analyzed. PU based nanocomposites with reinforcement of various fillers like silica nanoparticles, metal oxide nanoparticles, zeolite nanoparticles, carbon-based nanoparticles and metal organic framework-based nanoparticles are briefly discussed in this review.
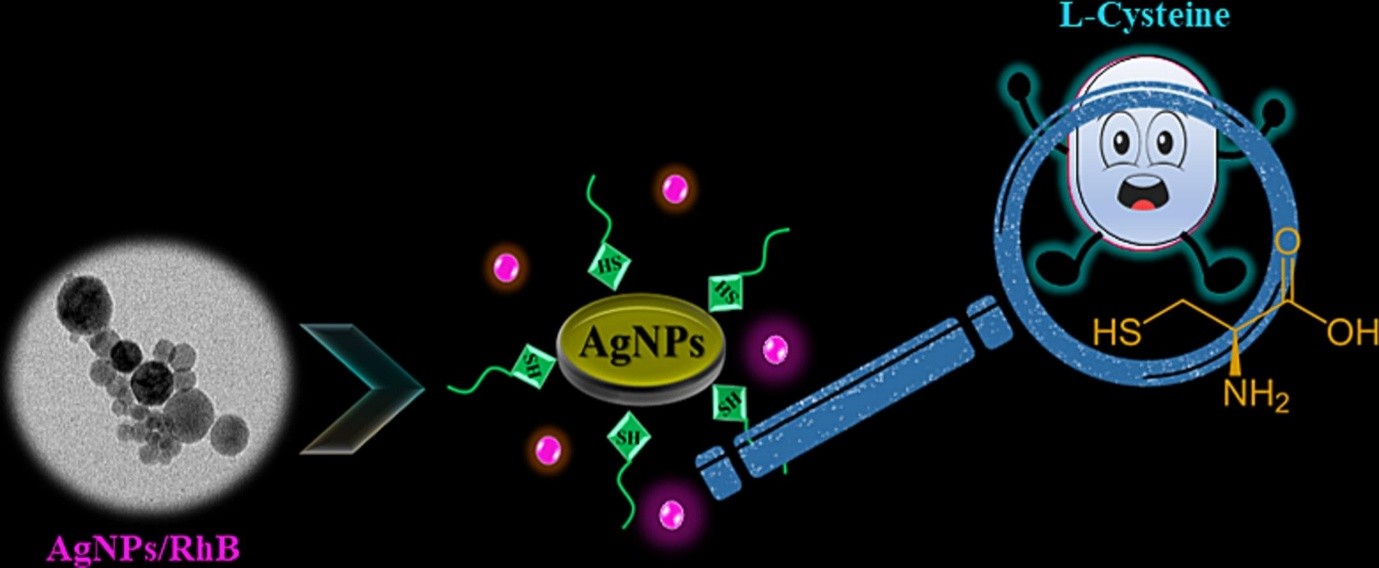
Rhodamine B embedded silver nanogranules for selective sensing of l-cysteine
Sensing of amino acid serves as the frontier research area for early diagnosis and monitoring various diseases. Among various amino acids, the sensing of L-Cysteine is much important for detection of human diseases like neurotoxic effect and coronary heart disease which arises due to excess of L-Cysteine. To address this, we propose a very simple method of L-Cys sensing via fluorescence “TURN ON” mechanism involving silver centred Rhodamine B nanogranules (AgNPs/RhB) stabilized via electrostatic interaction. The as-synthesized nanocomposite fluorescence probe shows highly selective sensing towards L-Cysteine aided by the preferential formation of stable covalent linkage between AgNPs and thiol group of L-Cys which is supported by FTIR and XPS study. The superior selectivity of L-Cysteine in presence of other amino acids and interactive ions with a limit of detection (LOD) of 1.084 µM and working linear range of 100–2200 µM makes the study a useful addition to the existing literature. The responsiveness of nanogranules to extreme conditions of ionic strength and pH further establishes its stability and suitability for present application. Moreover, the excellent recovery percentages obtained in real human serum samples establishes its effectiveness in diagnostic fields.
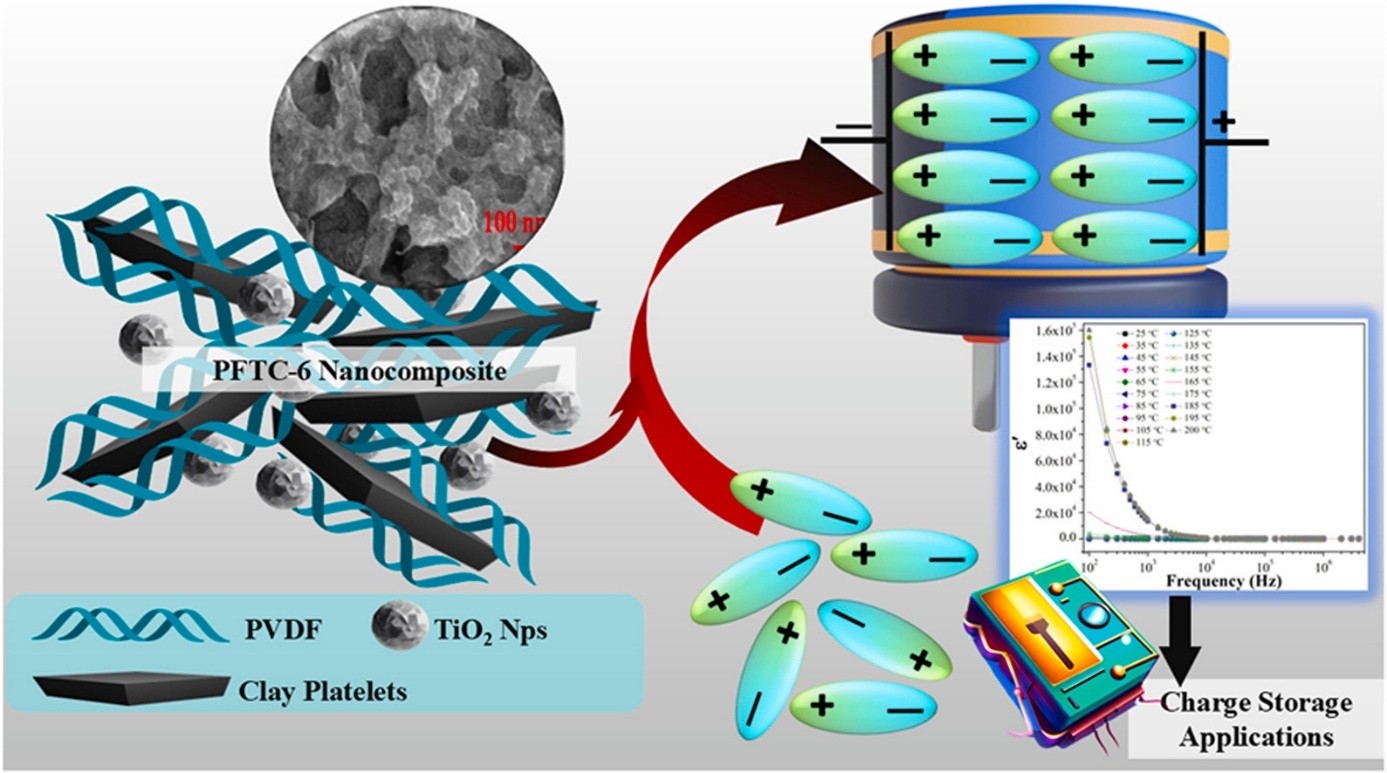
Effect of clay on dielectric behaviour of TiO2 embedded PVDF nanocomposite for charge storage applications
The work involves dielectric properties of PVDF/TiO2 and PVDF/TiO2/Clay nanocomposite synthesized via solution casting technique. The increased nucleation density attributed to PVDF, TiO2 and Cloisite® 30B NPs causes oriented planes that improve the crystallinity of the resultant nanocomposites. The morphological images prove the uniform deposition of TiO2 and Cloisite® 30B NPs in the ternary nanocomposite. Improved roughness of ternary nanocomposite is observed in AFM images causing huge charge-storing properties in the polymer-based nanocomposite. The highest ε' of PVDF/TiO2 and PVDF/TiO2/Clay nanocomposites are achieved as 2 × 103 and 1.4 × 104 at 1 kHz, respectively. The maximum ε′′ of PFTC-6 nanocomposite is found to be 4.04 at 1 kHz. This giant permittivity of the prepared ternary polymer-based nanocomposite could be a great pathway for the electronic industry. The PVDF/TiO2 nanocomposite shows maximum σac conductivity of 5.16 × 10−4 S/m and 5.87 × 10−4 S/m at 1 kHz and 3 MHz, meanwhile the PVDF/TiO2/Clay nanocomposite shows maximum σac conductivity of 3.37 × 10−3 S/m and 5.16 × 10−3 S/m at 1 kHz and 3 MHz, respectively. The high thermal stability and excellent dielectric behaviour of PVDF/TiO2/Clay nanocomposite prove its worth towards high performance in charge storage and electronic applications.